In navigating the Canadian educational landscape, prospective students often encounter the question: What sets universities apart from colleges? In a country known for its post-secondary institutions, understanding the distinctions between colleges and universities can help in making informed decisions about one’s post-secondary education options.
For example, in the United States, the term “college” is often used to refer to both undergraduate and graduate institutions. In Canada, the terms “college” and “university” refer to distinct types of post-secondary institutions and there are key differences between them.
What are Canadian college and university differences?
Degrees and Programs:
- Universities: Typically offer a wide range of undergraduate and graduate degree programs, including bachelor, master and doctoral degrees. Universities focus on academic and professional education and often engage in research activities.
- Colleges: Primarily provide diploma and certificate programs, as well as some degree programs (for example, some colleges offer nursing degrees). The emphasis at colleges is often on practical, hands-on training for specific careers or industries.
Academic Focus:
- Universities: Emphasize theoretical and academic aspects of education. They are known for research and scholarly activities, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in various fields.
- Colleges: Focus is on applied learning, preparing students for specific professions or trades. College programs are designed to equip students with practical skills for the workforce. Colleges can also offer the first two years towards a university degree.
Duration of Programs:
- Universities: Bachelor’s degrees typically take three to four years to complete, and advanced degrees can take additional years.
- Colleges: Programs are generally shorter in duration, ranging from a few months to a few years, depending on the level and type of programs.
Entrance Requirements:
- Universities: Generally have higher academic entrance requirements. They often require completion of specific high school courses and competitive grades.
- Colleges: Tend to have more accessible entry requirements. Some programs may have specific prerequisites, but overall, colleges are often more focused on practical skills development.
Culture and Atmosphere:
- Universities: Tend to have a more research-oriented and academic culture. There is often a greater emphasis on independent study and theoretical understanding.
- Colleges: Have a more hands-on and practical atmosphere. Class sizes may be smaller, and there may be a stronger connection between students and instructors.
It’s important to note that there can be variations between specific institutions, and some universities in Canada may also offer applied or vocational programs, while certain colleges may offer degree programs. Always check the specific offerings and characteristics of individual institutions to understand their unique features.

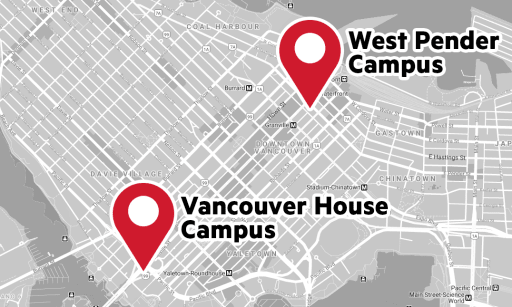
What is University Canada West?
University Canada West is a university for domestic and international students. Founded in 2004, it is a private higher education institution that provides university programs for graduate (Master of Business Administration) and undergraduate (Associate of Arts, Bachelor of Commerce, Bachelor of Arts in Business Communication) studies.
UCW is a Canadian university, but it’s two-year Associate of Arts (AA) diploma is similar to a college program in that with the university transfer credits earned, students can transfer into bachelor’s degree programs at UCW and all British Columbia degree-granting institutions, provided other admission requirements are met. Students can also use an AA as a credential to enter the labour market.
UCW’s bachelor and master degree programs are offered both on-campus and online, which creates flexibility for both domestic and international students.

Canada college and university differences FAQ
- What is the primary difference between universities and colleges in Canada?
- Canadian universities typically offer a broader range of academic programs, including undergraduate, graduate and professional degrees, along with a strong emphasis on research. Colleges, on the other hand, focus more on applied learning, offering diploma, certificate and some degree programs geared towards specific industries or career paths.
- How do the admission requirements differ between universities and colleges in Canada?
- Admission requirements for universities often include competitive academic grades, completion of specific high school courses, standardized test scores and sometimes supplementary application materials. For international students, there may be language proficiency requirements. Colleges generally have more accessible entry requirements, placing less emphasis on academic grades and more on practical skills or work experience relevant to the program of study.
- What are the implications for career outcomes when choosing between a university and a college in Canada?
- While attending Canadian universities or colleges can lead to successful careers, the choice between the two often depends on individual career goals and preferences. University graduates may have broader theoretical knowledge and research experience, making them well-suited for roles in academia, research or professions requiring advanced degrees. College graduates, on the other hand, are often equipped with practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific industries, making them attractive candidates for technical or vocational positions.
Published on March 15, 2024.